Creating a Virtual Database Server
In order to use a relational database environment, create virtual database servers. You can select the virtual database servers to create from various types according to the level of performance that is required, and you can configure settings such as automatic backups, as well.
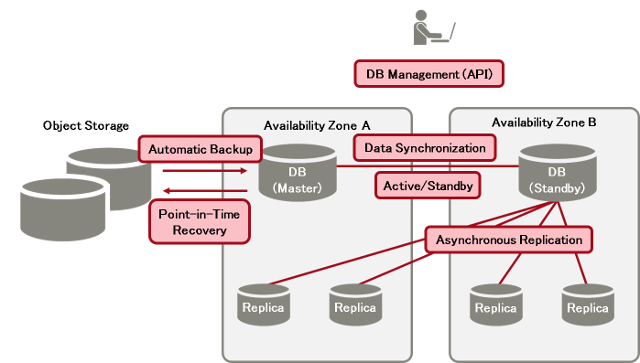
Functions to enhance the performance, availability, and reliability are provided based on the virtual database servers that are created.
Figure: Overall Layout of Database as a Service
Virtual Database Server Settings
Configure the virtual database servers to be created.
- Specification of the virtual database server name
-
Selection of the virtual database server type
Table 1. List of Provided Virtual Server Types (Flavors) (Standard CPU) Type Name Number of Virtual CPUs Memory (GB) C-2 2 4 C-4 4 8 C-8 8 16 C-16 16 32 S-1 1 4 S-2 2 8 S-4 4 16 S-8 8 32 S-16 16 64 M-1 1 8 M-2 2 16 M-4 4 32 M-8 8 64 M-16 16 128 XM-4 4 128 LM-1 1 16 LM-2 2 32 LM-4 4 64 LM-8 8 128 L-12 12 128 L-24 24 128 Table 2. List of Provided Virtual Server Types (Flavors) (High-Speed CPU) Type Name Number of Virtual CPUs Memory (GB) C2-2 2 4 C2-4 4 8 C2-8 8 16 C2-16 16 32 S2-1 1 4 S2-2 2 8 S2-4 4 16 S2-8 8 32 S2-16 16 64 M2-1 1 8 M2-2 2 16 M2-4 4 32 M2-8 8 64 M2-16 16 128 XM2-4 4 128 LM2-1 1 16 LM2-2 2 32 LM2-4 4 64 LM2-8 8 128 L2-12 12 128 L2-24 24 128 - Specification of the name of the availability zone where the server will be created
- Specification of the DB subnet group
- Specification of the DB parameter group
Data Area Settings
Specify the disk capacity and disk type that is used for the data area. Select the disk capacity from 10 GB to 10 TB, and the disk type from the following types.
| Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Standard (type M1) |
Use this in the following cases:
|
The following are included in the disk capacity used as the data area.
- The user data area of the PostgreSQL database
- The system data area of the PostgreSQL database
- The engine log area
- The transaction log area
- Temporary files such as sorts
Redundancy Settings
- Multi-DB option (Enable or Disable)
- Multi-AZ option (Enable or Disable)
| Multi-DB Option | Note | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disable | Enable | |||
| Multi-AZ Option | Disable | ✓ | ✓ |
The standby virtual database server is created within the same availability zone, according to the multi-DB option setting. Important: If the region has only one availability zone, be sure to specify "Disable".
|
| Enable | - | ✓ |
The standby virtual database server is created within another availability zone. Important: If "Enable" is specified for the multi-AZ option, be sure to specify "Enable" for the multi-DB option as well.
|
|
After the standby virtual database server is created, data is duplicated from the active server to the standby server synchronously, which ensures data redundancy.
- Data is duplicated from the data area connected to the virtual database server, on a per-data area basis.
- Data cannot be read from the standby server.
- As data is duplicated synchronously, write performance may be affected compared to when the redundancy settings are disabled.
Automatic Backup Settings
Configure automatic backup settings to perform a daily full backup of data and configuration files on the virtual database server. Items that you can specify are as follows.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Backup time | Specify a specific time as the start time of the backup (specify the time in UTC) |
| Backup retention period | Specify in the range from 0 to 10 (days). If you specify 0, automatic backup will not be performed. |
Automatic Maintenance Settings
If automatic maintenance is set, maintenance (setting modifications of the database virtual server that require restarting) will be performed automatically every week. You can also select whether or not to perform automatic maintenance.
Items that you can specify are as follows.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Maintenance time | Specify a specific time as the start time of maintenance (specify the time in UTC) |
| Automatic maintenance | Specify whether or not to perform automatic maintenance |
However, in automatic maintenance, updating of security and application of software patches are not performed. When performing application of patches, refer to Applying Patches to Database Virtual Servers.
Access Control
The security group function controls access to virtual database servers.
Database Settings
Configure settings for the database management master user, character codes, and other settings.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Master user name | Specify the database management user name |
| Master user password | Specify the password for the database management user |
| List of users for database connections | Specify as a list the user name, password, and the name of the database to which the user can connect |
| Character code | Specify the character code that is used in the database |
Points to Note
- Because virtual database servers are managed by the system, you cannot log in to virtual database servers by using SSH or remote desktop.
- The TCP timeout value of virtual database servers is one hour. This value cannot be changed.
- In the database service, the checksum functions of database engines are enabled.