Virtual Server for SAP
Virtual servers can be created for SAP applications as virtual environments supported by SAP.
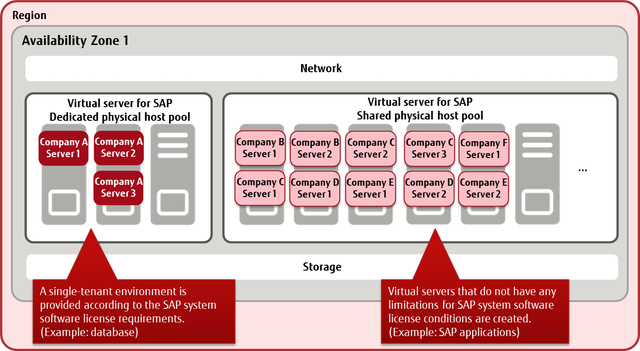
Functions Included
-
Compute
-
Enabling/disabling of an environment
Specify a project and availability zone, and set whether to enable the virtual server for SAP environment.
Note: If you disable this environment, you must delete all created virtual servers for SAP, images, and network resources in the project. -
A virtual server for SAP
- Creating/deleting a virtual server for SAP
- Startup/termination of a virtual server for SAP
- Restarting a virtual server for SAP
- Acquiring information for a virtual server for SAP
-
OS provision service
Use the images provided in List of Available OS of Virtual Server for SAP to create a virtual server for SAP.
You can use Windows Server Update Services and Windows Activation (KMS), which are common network services.
-
Software support service
The available functions and charge systems comply with .
-
Auto recovery of a virtual servers (Automatic failover)
If the server stops during an operation due to issues such as failure of the physical host machine at the data center, the virtual server that was operating on that host machine is automatically moved to a different host machine and the server operates there.
Note:- The automatic failover (automatic recovery) function is always enabled (it cannot be disabled). When automatic failover is completed, a notification email is sent to the overall administrator of the project the target resource belongs to. For details on notification emails, refer to Automatic Failover Notification Messages.
-
If Auto-Failover is performed while virtual servers are being started or stopped, they may have a different power status from the assumed status.
In such cases, manually perform the power operation for the virtual server. If the power status does not change within around 10 minutes, perform the power operation again.
-
Image management
Create private images from an existing virtual server for SAP and delete private images that have been created.
Tip: A private image that has been created can be used only in the activity zone in which it was created.Choose to disclose a created private image either within the project or within the domain.
-
-
Storage
-
Storage Type
There are the following types of storage.
Table 1. List of Storage Types Class Storage Type Standard Type M1 High Performance Type H2 Note: The storage type can be selected when adding a disk to a virtual server. You cannot change the storage type after a disk has been added.-
Standard Type
The standard type is efficient in cost performance.
Table 2. Purposes and Disk Sizes of the Standard Type Storage Type Purpose Disk Size M1 - When you deploy application data that requires frequent file access (reading and writing)
- When you handle a lot of large data files
0.1 - 2047 GB (in units of 0.1 GB) -
High Performance Type
For high performance type, the performance of the storage improves, as the disk size increases.
Table 3. Purposes and Disk Sizes of the High Performance Type Storage Type Purpose Maximum IOPS/GB Disk Size H2 For small-scale or medium-scale DBs, when storing application data that requires data throughput. 5 IOPS/GB *1 512 - 2047 GB (in units of 1 GB) *1: IOPS is calculated with a block size of 16 KB. Performance varies depending on the operating environment and other factors. There is no guarantee for a certain level of performance.
Note:-
The high performance type cannot be specified for the following. These are fixed as standard type.
- System storage
- Additional storage created when creating a virtual server
- Storage performance varies in proportion to the disk size. Therefore, a disk with a small storage size may not produce enough storage performance.
-
-
-
System Storage
System storage is provided as a system region for starting the OS. The size of system storage is determined according to the OS image selected in the OS provision service.
Standard type storage is used for system storage.
Table 4. List of System Storage Sizes (Eastern Japan Region 1, Western Japan Region 2) OS Type OS Provided Size Windows Windows Server 2016 SE 64bit English Version 180 GB Windows Server 2012 R2 SE 64bit English Version 180 GB Windows Server 2008 R2 SE SP1 64bit English Version 180 GB Windows Server 2016 SE 64bit Japanese Version 80 GB Windows Server 2012 R2 SE 64bit Japanese Version 80 GB Windows Server 2008 R2 SE SP1 64bit Japanese Version 80 GB -
Additional storage
Additional storage is provided for data archiving.
When adding storage to a virtual server, it is possible to select the storage type.
Table 5. Selectable Additional Storage Types and Sizes Storage Type Size Standard Type 0.1 - 2047 GB High Performance Type 512 - 2047 GB Table 6. List of Limiting Values Related to Additional Storage Item Limiting Values Number of Storage Systems 1 - 55
-
Snapshot function
This function is used to take, restore, and delete snapshots for existing virtual servers for SAP.
Note: If you delete a virtual server for SAP in which snapshots are taken, the snapshots will also be deleted.Table 7. List of Limiting Values Related to Snapshots Item Limiting Values Number of Snapshots Taken Maximum 10 generations
-
-
Network
-
Network resource management
For virtual networks and subnets that have been created, you can assign and release network resources for the virtual server for the SAP environment.
Tip: You can use private IP addresses and gateway IP addresses by assigning network resources. -
Adding/deleting ports
Note:- If you add or delete ports, also modify the network adapter settings on the OS as appropriate.
- You cannot use security group functions.
Table 8. List of Limiting Values Related to Adding a Port Item Limiting Values Number of Ports that Can Be Added 1 - 9
-
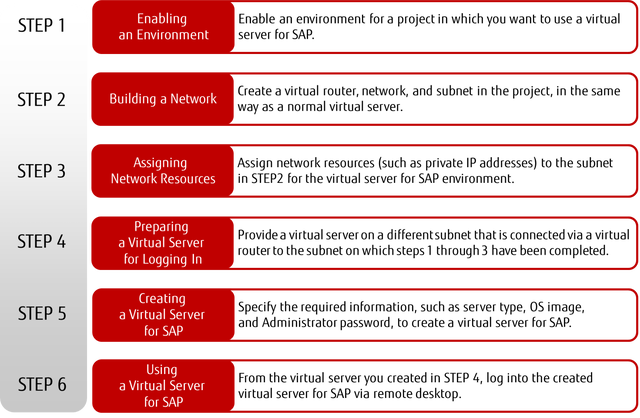
How to Use This Service
Figure: How to Use a Virtual Server for SAP
Points to Note
- An auto-scaling function is not provided.
- A virtual server import function is not provided.
- You cannot assign a global IP address to a virtual server for SAP. Use the service via a normal virtual server.
- Only a virtual server for SAP can be created in a subnet that has had its settings modified for use with a virtual server for SAP. A normal virtual server cannot be created.
- A virtual server for SAP cannot be targeted for a load balancer to distribute the load.
- This server cannot be created with a template.
-
If a physical host in a data center experiences an abnormality, the virtual server for SAP running on the target host is automatically migrated. During this migration, access to the target virtual server and business applications will be temporarily suspended.