Auto-Scaling Settings
You can set a scaling group that has specific conditions (such as the number of virtual servers) in the stack definition in order to automatically control the increase and decrease of resources.
Figure: Overview of Auto-Scaling
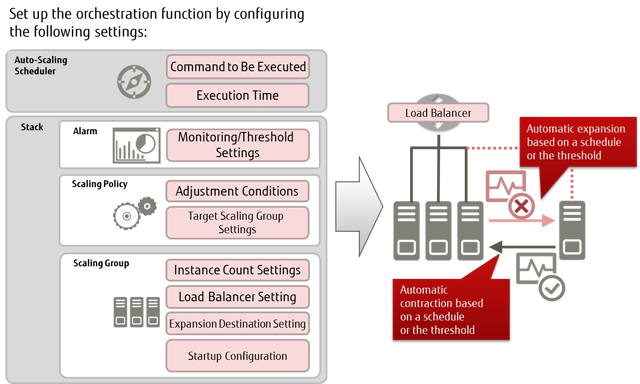
You can configure the auto-scaling function settings as follows.
Scaling Group Management Function
Set the following items to create scaling groups and register them in the stack. You can also configure settings for the health check function, which detects abnormality on scaled-out virtual servers and starts recovery automatically.
| Item | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Cool down period (Cooldown) | Specify this setting, in seconds, to prevent the next scaling operation from starting immediately after the previous scaling operation was completed | |
| Startup configuration name (LaunchConfiguration) | Specify the name of a startup configuration to start the virtual server | Yes |
| Load balancer name (LoadBalancerNames) | Specify as a list the names of the load balancers that are included in the scaling operation | |
| Maximum number (MaxSize) | Specify the maximum number of virtual servers to be scaled | Yes |
| Minimum number (MinSize) |
Specify the minimum number of virtual servers to be scaled Tip: This is the number of servers that are created initially when the stack is registered.
|
Yes |
| Availability zone name (AvailabilityZones) | Specify the name of the availability zone where you intend to create the scaling group | Yes |
| Subnet ID list (VPCZoneIdentifier) | Specify as a list the subnet IDs that exist in the availability zone that you specified for the availability zone name |
Scaling Policy Settings
Specify the following items to set a scaling policy.
| Item | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Scaling type (AdjustmentType) |
Specify how to increase or decrease the number of virtual servers by selecting one of the following types
|
Yes |
| Scaling group name (AutoScalingGroupName) | Specify the name of the scaling group on which you intend to set the scaling policy | Yes |
| Cool down period (Cooldown) | Specify this setting, in seconds, to prevent the next scaling operation from starting immediately after the previous scaling operation was completed | |
| Scaling value (ScalingAdjustment) |
Specify the scaling adjustment value according to the type that you specify for the scaling type Example: When you set the scaling type as "ChangeInCapacity" and set the change value as "-1," a virtual server will be deleted when the policy is applied |
Yes |
Startup Configuration Settings
Define the settings for when a scaling policy is applied and the virtual servers that are added are actually started.
| Item | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Image ID (ImageId) | Specify the ID or name of the image to be used on the virtual server to be started | Yes |
| Virtual server type (InstanceType) | Specify the type name (flavor name) of the virtual server to be started | Yes |
| Key name (KeyName) | Specify the name of the key pair that is set on the virtual server to be started | |
| Security group (SecurityGroups) | Specify as a list the security group names to be set on the virtual server to be started | |
| User data (UserData) | Specify the user data to be executed when a virtual server is started | |
| List of block storage device mapping settings (BlockDeviceMappingsV2) | Describe the block device mapping settings so that the device will be attached as block storage to the virtual server to be started |
Support of the Alarm Function
The alarm setting of the monitoring service specifies a scaling policy as an action to be taken when the value reaches the threshold. You can adjust auto-scaling according to the workload by setting the thresholds for alarms to call different scaling policies.
Example of Setting Auto-Scaling
An example of a stack definition that describes conditions for auto-scaling is shown below. In this example, the conditions are set as described below.
-
The following are defined for the scaling group:
- Specification of a load balancer in order to distribute the load on the auto-scaled virtual servers (balance the traffic load to port 80 (HTTP))
- Specification of the maximum number of virtual servers as three
- Specification of the minimum number of virtual servers as two
- Specification of the subnet to which auto-scaled virtual servers are connected
- Specification of the startup configuration (specification of values by using variables that are declared in the parameters section)
-
The following policies are defined as the scaling policies:
- web_server_scaleout_policy: Specification of "ChangeInCapacity" for the scaling type, and setting of one (+1) for the number of virtual servers to be added when the alarm is raised
- web_server_scalein_policy: Specification of "ChangeInCapacity" for the scaling type, and setting of one (-1) for the number of virtual servers to be deleted when the alarm is raised
-
The following two alarms are defined as the alarms:
- cpu_alarm_high: Application of web_server_scaleout_policy when a CPU usage rate of higher than 50% that continues for one minute or more is detected
- cpu_alarm_low: Application of web_server_scalein_policy when a CPU usage rate of 15% or lower that continues for one minute or more is detected
Example of stack definition:
heat_template_version: 2013-05-23
description:
Autoscaling sample template.
parameters:
az:
type: string
default: jp-east-1a
param_image_id:
type: string
# ImageID of CentOS
default: 1234abcd-5678-ef90-9876-fedc5432dcba
param_flavor:
type: string
default: standard
key_name:
type: string
description: SSH key to connect to the servers
default: sample_keypair00
autoscale_security_group:
type: comma_delimited_list
default: sample_SG00
resources:
web_server_group:
type: FCX::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroup
properties:
AvailabilityZones: [{get_param: az}]
LaunchConfigurationName: {get_resource: launch_config}
MinSize: '2'
MaxSize: '3'
# subnet ID for auto-scaling
VPCZoneIdentifier: [38e6630f-3257-4ee8-a006-f6d57ceaa2c3]
LoadBalancerNames:
- {get_resource: fj_elb}
launch_config:
type: FCX::AutoScaling::LaunchConfiguration
properties:
ImageId: { get_param: param_image_id }
InstanceType: { get_param: param_flavor }
KeyName: {get_param: key_name}
SecurityGroups: {get_param: autoscale_security_group}
BlockDeviceMappingsV2: [{source_type: 'image', destination_type: 'volume', boot_index: '0', device_name: '/dev/vda', volume_size: '40', uuid: {get_param: param_image_id}, delete_on_termination: true}]
fj_elb:
type: FCX::ExpandableLoadBalancer::LoadBalancer
properties:
# subnet ID for auto-scaling
Subnets: [38e6630f-3257-4ee8-a006-f6d57ceaa2c3]
Listeners:
- {LoadBalancerPort: '80', InstancePort: '80',
Protocol: 'HTTP', InstanceProtocol: 'HTTP' }
HealthCheck: {Target: 'HTTP:80/healthcheck', HealthyThreshold: '3',
UnhealthyThreshold: '5', Interval: '30', Timeout: '5'}
Version: 2014-09-30
Scheme: internal
LoadBalancerName: fjsampleELBaz1
web_server_scaleout_policy:
type: FCX::AutoScaling::ScalingPolicy
properties:
AdjustmentType: ChangeInCapacity
AutoScalingGroupName: {get_resource: web_server_group}
Cooldown: '60'
ScalingAdjustment: '1'
web_server_scalein_policy:
type: FCX::AutoScaling::ScalingPolicy
properties:
AdjustmentType: ChangeInCapacity
AutoScalingGroupName: {get_resource: web_server_group}
Cooldown: '60'
ScalingAdjustment: '-1'
cpu_alarm_high:
type: OS::Ceilometer::Alarm
properties:
description: Scale-out if the average CPU > 50% for 1 minute
meter_name: fcx.compute.cpu_util
statistic: avg
period: '60'
evaluation_periods: '1'
threshold: '50'
alarm_actions:
- {get_attr: [web_server_scaleout_policy, AlarmUrl]}
matching_metadata: {'metadata.user_metadata.groupname': {get_resource: 'web_server_group'}}
comparison_operator: gt
cpu_alarm_low:
type: OS::Ceilometer::Alarm
properties:
description: Scale-in if the average CPU < 15% for 1 minute
meter_name: fcx.compute.cpu_util
statistic: avg
period: '60'
evaluation_periods: '1'
threshold: '15'
alarm_actions:
- {get_attr: [web_server_scalein_policy, AlarmUrl]}
matching_metadata: {'metadata.user_metadata.groupname': {get_resource: 'web_server_group'}}
comparison_operator: lt