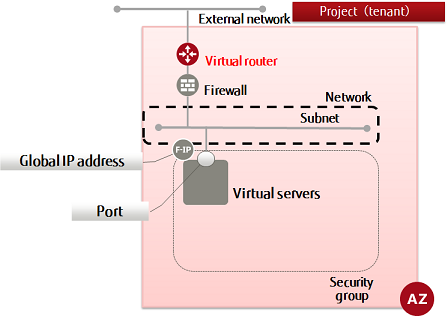
This section explains how to create a virtual router to either connect a network with an external network or to connect networks internally.
-
Set the environment variables below as follows:
$ ROUTER_NAME=<newRouterName (any)>
$ AZ=<availabilityZoneName>
-
Execute the API.
$ curl -Ss $NETWORK/v2.0/routers -X POST \
-H "X-Auth-Token: $OS_AUTH_TOKEN" -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"router": {"name": "'$ROUTER_NAME'", "tenant_id": "'$TENANT_ID'",
"availability_zone": "'$AZ'"}}' | jq .
The following response is output:
{
"router": {
"status": "ACTIVE",
"external_gateway_info": null,
"name": "<newVirtualRouterName>",
"admin_state_up": true,
"tenant_id": "<projId>",
"id": "<newVirtualRouterId>",
"availability_zone": "<specifiedAvailabilityZone>"
}
}
For the availability zones, AZ1 is expressed as "jp-east-1a", and AZ2 is expressed as "jp-east-1b".
-
Execute the following API to check that the virtual router was created properly:
$ curl -Ss $NETWORK/v2.0/routers -X GET \
-H "X-Auth-Token: $OS_AUTH_TOKEN" | jq .
If a list including the virtual router name that you specified is output, as follows, that means the virtual router was created successfully.
{
"routers": [
...
{
"status": "ACTIVE",
"external_gateway_info": null,
"name": "<newVirtualRouterName>",
"admin_state_up": true,
"tenant_id": "<projId>",
"id": "<newVirtualRouterId>",
"availability_zone": "<specifiedAvailabilityZone>"
},
...
]
}
Refer to the information changes of the virtual router (attached) for information on how to add a subnet using the information change feature of the virtual router.