Creating a virtual server (CentOS and port specification)
This section explains how to specify a port (private IP address) and create a virtual server (CentOS).
Refer to "Creating a virtual server (CentOS and DHCP retrieval)" for details on retrieving a port (private IP address) using DHCP.
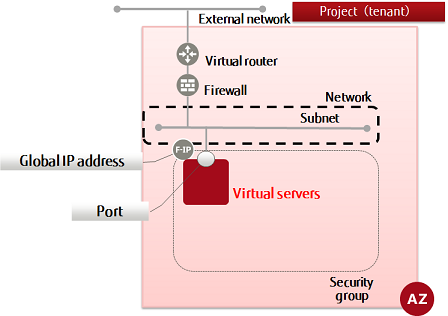
-
Set the environment variables below as follows:
$ VM_NAME=<virtualServerName> (any)
$ FLAVER_ID=<specOfVirtualServer> (listed flavor ID)
$ VOL_SIZE=30
$ DEVICE_NAME=<blockStoragePath> (specify using "/dev/vda" format)
$ IMAGE_REF_ID=839c1db6-738c-4e2b-9a1d-c14977564203<imgIdOfCentos>
$ SOURCE=<blockStorageType>
$ DESTINATION=<connectionDestinationVol>
$ ISDELETE=<volDeletion> (specify 1 to delete volumes created during creation of the virtual server, or 0 otherwise)
$ KEYNAME=<keyPairName>
$ INSTANCE_MAX=<maxNumOfServers>
$ INSTANCE_MIN=<minNumOfServers>
$ PORT_ID=<portIdToBeSpecified>
-
Execute the following API:
$ curl -Ss $COMPUTE/v2/$PROJECT_ID/servers -X POST \ -H "X-Auth-Token: $OS_AUTH_TOKEN" -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"server": {"name": "'$VM_NAME'", "imageRef": "", "flavorRef": "'$FLAVER_ID'", "block_device_mapping_v2": [ {"boot_index": "0", "uuid":"'$IMAGE_REF_ID'", "volume_size": "'$VOL_SIZE'", "device_name": "'$DEVICE_NAME'", "source_type": "'$SOURCE'", "destination_type": "'$DESTINATION'", "delete_on_termination": '$ISDELETE'} ] , "key_name": "'$KEYNAME'", "max_count": '$INSTANCE_MAX', "min_count": '$INSTANCE_MIN', "networks": [{"port": "'$PORT_ID'"}] }}' | jq .The following response is output:
{ "server": { "security_groups": [ { "name": "default" } ], "OS-DCF:diskConfig": "MANUAL", "id": "<newVirtualServerId>", "links": [ { "href": "http://10.3.0.201/v2/<projId>/servers/<newVirtualServerId>", "rel": "self" }, { "href": "http://10.3.0.201/<projId>/servers/<newVirtualServerId>", "rel": "bookmark" } ] } } -
Execute the following API to check the virtual server that you created:
$ curl -Ss $COMPUTE/v2/$PROJECT_ID/servers/detail -X GET \ -H "X-Auth-Token: $OS_AUTH_TOKEN" | \ jq '.servers[] | {status: .status, network_name: .addresses | keys, key_name: .key_name, flavor_id: .flavor | .id, vm_id: .id, security_group: .security_groups[] | .name, name: .name, }'If a list including the virtual server name that you specified is output, as follows, that means the virtual server was created successfully.
... { "status": "<statusOfVirtualServer>", "network_name": [ "<connectedNetworkName>" ], "key_name": "<keyPairName>", "flavor_id": "<flavorId>", "vm_id": "<virtualServerId>", "security_group": "<secGroupName>", "name": "<virtualServerName>" } ...