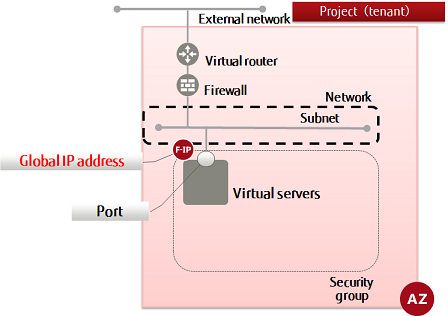
This section explains how to retrieve a global IP address for accessing virtual resources from the Internet and assign it to a virtual server.
A single call to the API can perform these two steps at the same time.
-
Set the environment variables below as follows:
$ NETWORK_ID=<networkId> (specify the external network ID of the availability zone where the virtual server is located)
$ VM_PORT_ID=<virtualServerId>
-
Execute the following API:
$ curl -Ss $NETWORK/v2.0/floatingips -X POST \
-H "X-Auth-Token:$OS_AUTH_TOKEN" -H "Content-Type:application/json" \
-d '{"floatingip":{"floating_network_id":"'$NETWORK_ID'",
"port_id":"'$VM_PORT_ID'", "availability_zone": "'$AZ'"}}' | jq .
The following response is output:
{
"floatingip": {
"router_id": "<virtualRouterIdOfDefaultGateway>",
"status": "DOWN",
"tenant_id": "<projId>",
"floating_network_id": "<externalNetworkAddr>",
"fixed_ip_address": "<privateIpAddr>",
"floating_ip_address": "<globalIpAddr>",
"port_id": "<specifiedPortId>",
"id": "<globalIpAddrId>",
"availability_zone": "<availabilityZone>"
}
}
For the availability zones, AZ1 is expressed as "jp-east-1a", and AZ2 is expressed as "jp-east-1b".
-
Execute the following API to check the global IP address that you created:
$ curl -Ss $NETWORK/v2.0/floatingips.json -X GET \
-H "X-Auth-Token:$OS_AUTH_TOKEN" -H "Content-Type:application/json" \
| jq .
If a list including the global IP address that you newly assigned is output, as follows, that means the address was created successfully.
{
"floatingips": [
...
{
"router_id": "<virtualRouterIdOfDefaultGateway>",
"status": "<status>",
"tenant_id": "<projId>",
"floating_network_id": "<externalNetworkAddr>",
"fixed_ip_address": "<privateIpAddr>",
"floating_ip_address": "<globalIpAddr>",
"port_id": "<portId>",
"id": "<globalIpAddrId>",
"availability_zone": "<availabilityZone>"
}
...
]
}